Definition:
A birth defect in which the major artery from the heart (the aorta) is narrowed somewhere along its length, most commonly just past the point where the aorta and the subclavian artery meet.
Alternative Names:
Aortic coarctation
Causes, incidence, and risk factors:
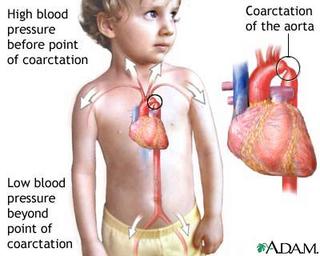
Coarctation means narrowing; aortic coarctaction is a birth defect (congenital disorder) in which a portion of the aorta is narrowed. The aorta is the source blood vessel for many arteries, which supply the body with blood and nutrients.
Aortic coarctation causes low blood pressure and low blood flow in the arteries that branch off below the narrow spot; high blood pressure occurs in the arteries that branch off closer to the heart. As a result, aortic coarctation often leads to high blood pressure in the upper body and arms (or one arm) and low blood pressure in the lower body and legs.Aortic coarctation is more common in some genetic conditions, such as Turner's syndrome, but it can also be associated with congenital abnormalities of the aortic valve, such as a bicuspid aortic valve.Aortic coarctation occurs in approximately 1 out of 10,000 people. It is usually diagnosed in children or adults under 40.
No comments:
Post a Comment